Geothermal Loops Slash HVAC Bills by 60 Percent
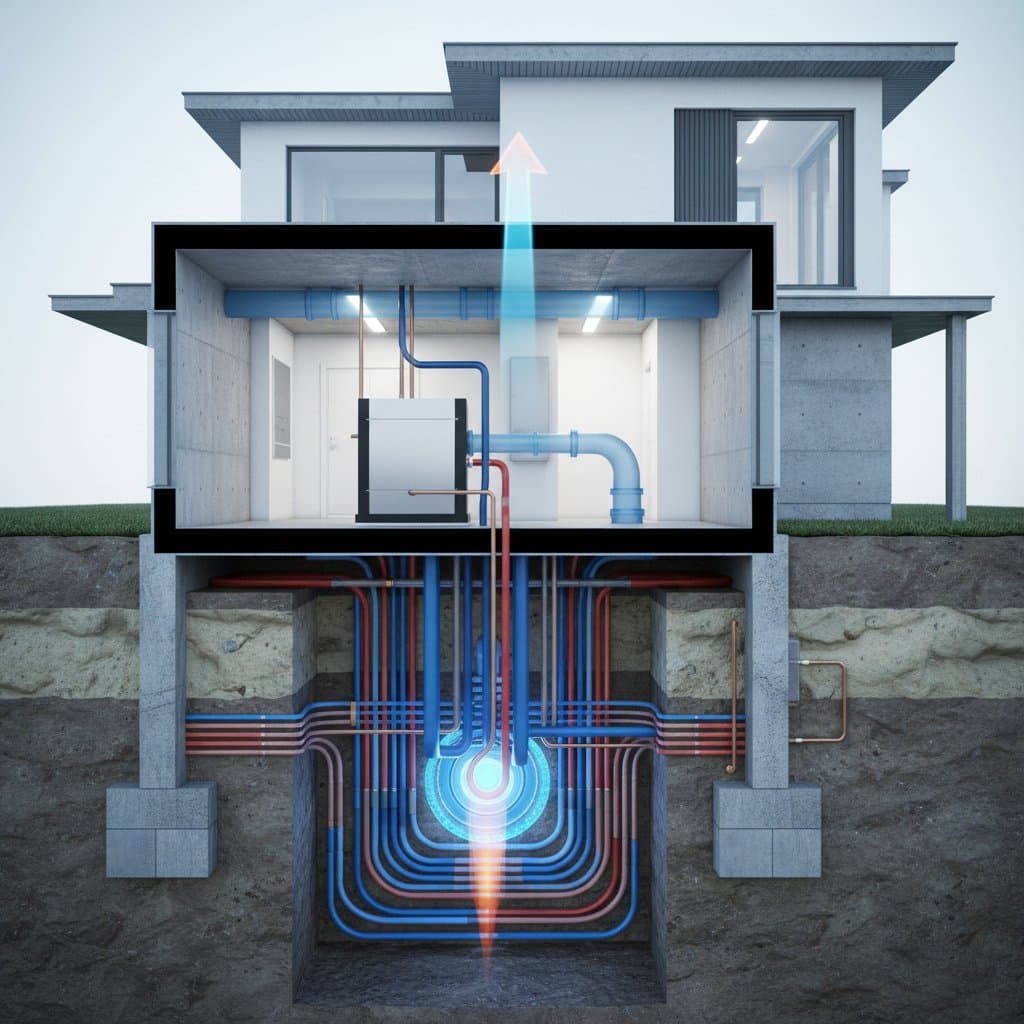
Geothermal heating and cooling systems represent a highly efficient method to lower energy use and utility expenses. These systems exchange heat with the consistent underground temperatures to achieve reductions in HVAC bills of up to 60 percent, all while delivering steady comfort throughout the seasons. The following sections detail the mechanics of geothermal loops, the installation process, and factors to consider for suitability on a specific property.
Key Takeaways
- Installation cost: Total expenses average between $18,000 and $35,000, allocated as approximately 40 percent for materials, 45 percent for labor, and 15 percent for equipment and permits.
- Loop depth and length: Vertical configurations demand 150 to 300 feet per ton of capacity, whereas horizontal setups require 250 to 500 feet per ton.
- Energy savings: Property owners typically realize 40 to 60 percent decreases in heating and cooling costs relative to traditional systems.
- Installation time: Residential installations generally span 7 to 14 days, influenced by soil type and loop design.
- Efficiency rating: Geothermal heat pumps commonly attain Coefficient of Performance (COP) ratings from 3.5 to 5.0, indicating strong energy transfer effectiveness.
Planning Your Geothermal Installation
Thorough preparation before any groundwork guarantees that the system matches the property's needs in size and configuration.
Evaluating Site Conditions
Soil composition plays a critical role in system performance. Sandy or loamy soils facilitate superior heat conduction, whereas rocky or arid soils might necessitate extended loop lengths to maintain efficiency. The presence of groundwater enhances conductivity in moist environments, thereby optimizing overall operation. Horizontal loops demand ample open space, making vertical loops preferable for compact lots. Systems excel in areas with pronounced seasonal temperature variations for heating or cooling.
Permits and Building Codes
Local authorities often mandate approvals for geothermal projects involving drilling or excavation. Contact the municipal building office to confirm regulations on borehole depths, circulating fluid types, and safeguards for the environment. Experienced contractors manage these steps to ensure compliance.
Cost Considerations
Initial investments exceed those of standard HVAC units, yet substantial energy reductions offset the outlay within 5 to 10 years via diminished utility payments. Availability of regional incentives, such as rebates and federal tax credits, accelerates the return on investment and makes adoption more accessible.
Preparing the Site and Installing the System
Engage a qualified contractor to analyze soil properties and outline the loop arrangement prior to any digging.
-
Excavation or Drilling
Horizontal designs involve digging trenches to the required depth, while vertical approaches use drilling equipment to create boreholes separated by 10 to 20 feet. -
Loop Placement and Connection
Install high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes, conduct pressure tests, and connect them via fusion to establish a secure, closed loop. -
Backfilling and Grouting
Refill trenches or boreholes with materials that promote thermal conductivity, enhancing heat exchange and safeguarding the piping. -
System Connection to Heat Pump
Link the underground loop to the indoor heat pump using insulated lines for supply and return. -
Testing and Commissioning
Perform pressure checks, remove air from the system, and adjust components to achieve peak functionality.
Projects in challenging terrains, such as those with solid rock or requiring deep bores, may extend beyond the typical two-week timeline.
Troubleshooting Common Challenges
System performance can occasionally falter due to specific issues. Reduced output often stems from air pockets in the loop or insufficient fluid volume; professionals can address these through flushing and refilling. Elevated running costs might result from suboptimal thermostat configurations or buildup on heat exchangers, resolvable via calibration and cleaning. Unusual noises or vibrations warrant examination of pumps and mounting stability. Imbalances in temperature distribution across zones typically require fine-tuning of control valves.
Routine inspections prevent escalation, with most problems handled via targeted maintenance rather than full replacements.
When to Call a Professional
Seek expert assistance if the system exhibits persistent inefficiencies, such as unexplained spikes in energy use or inconsistent temperatures. Professionals equipped with diagnostic tools can identify issues like refrigerant leaks or electrical faults that demand specialized repairs. Annual servicing by certified technicians ensures longevity and compliance with warranties, avoiding costly downtime during peak seasons.
Maintaining Your Investment
Regular upkeep preserves the system's efficiency and extends its service life, often exceeding 25 years for loops and 10 to 15 years for heat pumps. Schedule yearly inspections to check fluid levels, clean filters, and verify pump operation. Monitor for signs of wear, such as reduced flow rates, and address them promptly to sustain the 40 to 60 percent savings. By integrating simple habits like proper zoning and seasonal adjustments, owners maximize returns while minimizing environmental impact through reduced fossil fuel reliance.